D
Devin
January 26, 2026
Project Overview
Robot Agent is built on MiniMax M2.1 text model and Pi05 VLA (Vision-Language-Action) model, enabling natural language-driven robotic arm manipulation in the LIBERO simulation environment.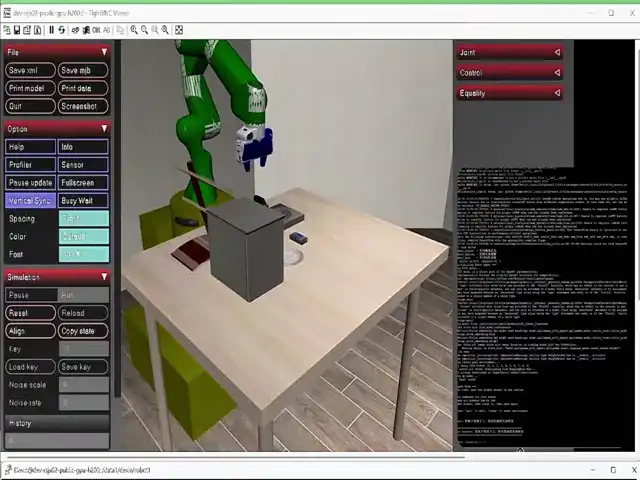
MiniMax M2.1 Task Planning
MiniMax M2.1 Task Planning
Understands user’s natural language instructions, decomposes complex tasks into executable steps, and coordinates multi-step task execution.
MiniMax MCP Visual Understanding
MiniMax MCP Visual Understanding
Uses MCP to invoke visual understanding capabilities, analyze scene images, verify task execution results, and enable closed-loop feedback control.
Pi05 VLA Action Execution
Pi05 VLA Action Execution
A vision-language-action model based on PaliGemma that generates precise robotic arm control actions based on scene images and task instructions.
LIBERO Simulation Environment
LIBERO Simulation Environment
Executes various robot manipulation tasks in a simulation environment powered by the MuJoCo physics engine.
System Architecture
| Module | Technology | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Task Planning | MiniMax M2.1 | Understand user intent, decompose tasks |
| Visual Understanding | MiniMax MCP | Scene analysis, result verification |
| Action Execution | Pi05 VLA | Vision-Language-Action model |
| Simulation | LIBERO / MuJoCo | Robot manipulation simulation |
Quick Start
Install Dependencies
| Dependency | Description |
|---|---|
| LeRobot | HuggingFace robotics library (included) |
| MuJoCo | DeepMind physics simulation engine |
| LIBERO | Robot manipulation simulation benchmark |
| MCP | Model Context Protocol client |
Supported Tasks
In the LIBERO Goal scenario, the Agent supports the following 10 manipulation tasks:| # | Task Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | open the middle drawer of the cabinet | Open the middle drawer of the cabinet |
| 2 | put the bowl on the stove | Place the bowl on the stove |
| 3 | put the wine bottle on top of the cabinet | Place the wine bottle on top of the cabinet |
| 4 | open the top drawer and put the bowl inside | Open the top drawer and put the bowl inside |
| 5 | put the bowl on top of the cabinet | Place the bowl on top of the cabinet |
| 6 | push the plate to the front of the stove | Push the plate to the front of the stove |
| 7 | put the cream cheese in the bowl | Put the cream cheese in the bowl |
| 8 | turn on the stove | Turn on the stove |
| 9 | put the bowl on the plate | Place the bowl on the plate |
| 10 | put the wine bottle on the rack | Place the wine bottle on the rack |
Core Code Analysis
Agent Tool Definitions
The Agent interacts with the environment through two core tools:MiniMax M2.1 Task Planning
Using Anthropic-compatible interface to call MiniMax M2.1:MCP Visual Understanding
Using MCP to invoke MiniMax visual understanding for task verification:Technical Details
Pi05 Model Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Base Model | PaliGemma |
| Input | 2 camera images + robot arm state + language instruction |
| Output | 7-dim action (end-effector position delta + orientation delta + gripper) |
| Control Frequency | 10Hz |
| Max Steps | 280 steps/task |
Agent Workflow
- User Input: Receive natural language instructions
- Task Planning: MiniMax M2.1 understands intent and maps to supported tasks
- Action Execution: Pi05 VLA generates robotic arm control sequences
- Result Verification: MCP visual understanding analyzes the scene to confirm task completion
- Feedback Loop: If verification fails, automatically retry the task
FAQ
API call error 'Invalid API Key'
API call error 'Invalid API Key'
Check if
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY is correctly set to your MiniMax API Key.Model loading failed
Model loading failed
- Check if
HF_TOKENis configured - Check if
MODEL_PATHpath is correct
MCP visual understanding error
MCP visual understanding error
Make sure you have installed:
pip install mcp and the uvx command is available.Visualization window not showing
Visualization window not showing
Set
export DISPLAY=:2 (VNC) or ensure you have an X11 environment.Application Extensions
Based on the current architecture, developers can explore the following directions:- Multi-task Chaining: Implement automatic decomposition and sequential execution of complex tasks
- Failure Recovery: Enhance error detection and automatic recovery capabilities
- Real-world Deployment: Transfer simulation policies to physical robotic arms
- Multi-modal Interaction: Combine speech recognition to enable voice-controlled robots
Summary
In this tutorial, we demonstrated how to build an intelligent robot using MiniMax M2.1 and MCP visual understanding:- MiniMax M2.1 understands user intent and converts natural language instructions into specific manipulation tasks
- MiniMax MCP provides visual understanding capabilities to verify task execution results and enable closed-loop control
- Pi05 VLA serves as the underlying executor, generating precise robotic arm actions based on visual input
- LIBERO/MuJoCo provides a realistic physics simulation environment